The Critical Distinctions of CBDCs and Cryptocurrencies You Need To Know
The subject of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) is more pervasive than ever, with governments worldwide rushing to roll out their CBDCs, advocating that central bank digital currencies are like cryptocurrencies, only better. Citizens all over the world know this statement is false and vehemently oppose this new monetary system by lodging petitions and protests. However, a substantial proportion of society doesn’t recognize or even comprehend this age of digital technology.
Today we’ll look at the difference between CBDCs and cryptocurrency and how they cannot be compared. That’s because one system will be used to enslave us, and the other will give us freedom and sovereignty.
When Did It All Start?
The two financial technologies are rooted in various digital currency initiatives, mostly coming into existence in the 1990s. The most significant difference is the digital currencies of that time were created to optimize payments primarily in a domestic setting. In other words, these digital currencies were intended to optimize the existing financial system by integrating with it.
An example is Finland’s eMoney system, Avant, in the 1990s, which was closely connected to its national currency and banking infrastructure. While some consider Finland’s eMoney to be the first CBDC, it is generally believed that the first actual CBDC to be released was the Bahamian Sand Dollar in October 2020. Although now, almost every country is actively working on a CBDC of some kind.
In contrast to CBDCs, cryptocurrencies were initially created to replicate or even replace the existing financial system. In many cases, this meant they were internationally available to anyone with an internet connection. Two examples are David Chaum’s Ecash in the 1980s and Adam Back’s Hashcash in the 1990s. Today, Adam is the CEO of Blockstream, one of the largest Bitcoin-related companies.
Then along came Bitcoin in 2008, boasted as the first cryptocurrency, created by a pseudonymous individual or group called Satoshi Nakamoto. The first Bitcoin block contained a hidden message: "Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks.” This was the headline of The Times newspaper on January 3rd, 2009, the same day Bitcoin went live.

Bitcoin’s explicit intention is to replace the current financial system, and every prominent cryptocurrency that has come into being since that time shares this ethos. Whereas Bitcoin was created in response to the 2008 financial crisis, the CBDC was essentially created in response to cryptocurrencies. More to the point, CBDCs were created in response to alternative digital currencies of all kinds, be they public or private.
For example, China began developing its digital Yuan in response to the country's rapid growth of financial technology companies during the 2010s. Similarly, the United States started developing its digital dollar in response to Facebook's digital currency, Libra, which was revealed in 2019 but never made it off the ground. On the other hand, Indonesia began developing its digital Rupiah in response to cryptocurrencies after the last bull run in 2017.

Meanwhile, the Marshall Islands began developing its digital currency, dubbed the Marshallese sovereign, in response to developing CBDCs in other countries. Nevertheless, the common theme is centralized financial system control. This ultimately makes today's CBDCs different from their predecessors, which focused on payment optimization rather than centralized control.
As such, we can define CBDCs as a type of digital currency centrally controlled by the government and requiring permission. Alternatively, we can define cryptocurrencies as virtual currency that is not controlled by anyone and does not require permission.
CBDC’s and Cryptocurrency’s Underlying Implementations
Understanding how CBDCs and cryptocurrencies work under the hood is essential, starting with three definitions for the often misunderstood terms; Blockchain, Distributed Database (DDB), and Distributed Ledger technology. (DLT)
A blockchain is a specific type of distributed ledger technology. Notably, all Blockchains are distributed ledgers (DL), but not all distributed ledgers are blockchains. Permissionless or public blockchains are decentralized, meaning a single individual or institution does not control them. Instead, they are controlled by a vast network of unrelated individuals and institutions, so there's no single point of failure.
Distributed databases store data in a shared network rather than at a centralized location. This solution is for businesses that need to process huge amounts of structured and unstructured data, which could scale across networks. Consensus mechanisms such as Paxos or Raft control read/write permissions and establish secure communication channels among participants. However, these protocols assume that each participant cooperates in good faith, which limits their application to private networks under a centralized authority.
Distributed Ledgers (DL) are like DDB protocols in that they maintain a consensus about the existence and status of a shared set of facts but do not rely on this assumption of good faith. They achieve this by leveraging strong cryptography to decentralize authority. They are different from generic distributed databases in two fundamental ways:
1. The control of the read/write access is genuinely decentralized, whereas it remains logically centralized for distributed databases.
2. Data integrity can be assured in adversarial environments without employing trusted third parties, whereas distributed databases rely on trusted administrators.

These terms are good to know because many countries claim their CBDCs will use a blockchain. However, countries claiming their CBDCs will use a Blockchain will use a distributed database because the Central Bank will centrally control it. It's possible that the officials making these statements don't know the difference or don't care to make the distinction.
Some argue that the purpose of using the term ‘blockchain’ or ‘inspired by Bitcoin’ is to intentionally mislead the public into thinking the CBDC is just like a cryptocurrency. Although, it’s worth mentioning that a few regions seem to be planning to launch their CBDCs on cryptocurrency blockchains, such as the Marshall Islands, which has selected Algorand technology. But even then, it's likely that the central bank will still maintain total control of its CBDC because it would be issued as a token.
What Is The Difference Between Coins And Tokens?
As we continue to be enlightened by this technology, the two different cryptocurrencies are often misrepresented, so here are the definitions of crypto coins and tokens.
A cryptocurrency coin is native to its blockchain and is given as a reward to the miners (basically just powerful computers) that process transactions. Cryptocurrency coins also pay transaction fees on a cryptocurrency’s blockchain. For example, BTC is given as a reward to cryptocurrency miners that process transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain. These cryptocurrency miners also earned the transaction fees paid in BTC.
Conversely, a cryptocurrency token is a customizable digital asset that exists on a cryptocurrency’s blockchain. Unlike coins, which directly represent a proposed medium of exchange, crypto tokens represent an asset. These tokens can be held for value, traded, and staked to earn interest. Unlike coins, tokens can choose not to be bound to a single blockchain, gaining flexibility and becoming easier to trade.
Tokens are used with decentralized applications (DApps) and are usually built on top of an existing blockchain. One example is Markethive’s Hivecoin, currently being integrated into the Solana Blockchain. Cryptocurrency tokens can be used for all sorts of things and have led to some exciting applications, such as decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and emerging crypto ecosystems in social media and marketing.
The key takeaway here is that the creator of a cryptocurrency token can give themselves total control over the transfers of that token, the supply of that token, etc. Some stablecoins are cryptocurrency tokens that mirror the price of fiat currencies, primarily the US dollar. So, in the case of centralized stablecoins that are centrally controlled by the companies which issued them, any CBDCs issued as cryptocurrency tokens will likely work similarly.
The Economics Of CBDCs And Cryptocurrencies
For context, let’s look at the economics of the current financial system. Central banks worldwide are tasked with encouraging economic growth while keeping inflation under control. They do this by raising and lowering interest rates. When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes cheap, making saving less attractive. This incentivizes individuals and institutions to spend rather than save, which increases economic growth. However, it also increases inflation as more money is circulated with low-interest rates.
When interest rates are high, borrowing becomes expensive, making saving more attractive. This incentivizes individuals and institutions to save rather than spend, which lowers economic growth. However, it also decreases inflation as there is less money in circulation when Interest rates are high.
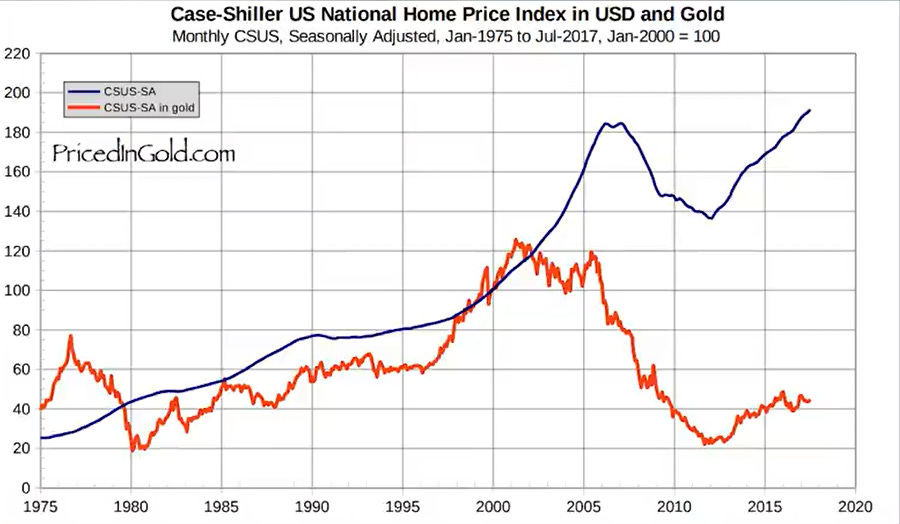
The big problem with this economic model is that money can easily be created, but taking it out of circulation is much more challenging. This inevitably leads to inflation in the long term. Long-term inflation wasn't a problem because fiat currencies were backed by gold. This limits how much money could be created in an economy because more gold had to be acquired to issue more money.
However, this limit was lifted when the gold standard collapsed in 1971. And since then, we've seen what can only be described as long-term inflation, with the prices of many assets exploding in fiat terms while staying the same when priced in gold.
However, it’s become clear that this inflation didn't show up in official inflation statistics until very recently because they have been adjusted and under-reported since they were introduced to make them seem less severe. This inflation is starting to appear in the official statistics, which means it's even worse than the authorities reveal.
Individuals and institutions took on record debt levels when interest rates were low, which means that raising interest rates too high would result in an economic catastrophe as these individuals and institutions would be unable to pay back their debts.
It’s also apparent that many governments have record debt levels, and we're already seeing the first signs of default in some countries. In short, the money supply has grown so much that inflation is off the charts. And raising interest rates is not an option because of all the debt built up in the financial system over the years.
CBDC Economics
From the banks' perspective, CBDCs offer a solution to this situation. This is because, in a CBDC system, one of the many features is that it'll be possible for the central bank to destroy money as well as issue it easily. For starters, there'll be two types of CBDCs. Select individuals and financial institutions will use wholesale CBDCs, and regular folks like you and I will use Retail CBDCs.
This means there will be one financial system for the people in power and another for everyone else. Now, in addition, to being able to create and destroy money, Retail CBDCs will make it possible for central banks to;
Freeze CBDC holdings.
Set limits on CBDC holdings.
Set expiry dates on CBDC holdings.
Set location limits for where CBDCs can be spent.
Set time limits for when CBDCs can be spent.
Set limits on how much CBDC can be spent.
Decide what can and can't be purchased with CBDCs.
Add a tax to every CBDC transaction.
Automatically flag or block suspicious CBDC transactions.
Create custom CBDC limits for different individuals and institutions, depending on whatever criteria they decide.
Implement negative interest rates by gradually deleting unspent CBDC holdings over time.
Financial institutions have openly discussed all the above features of CBDCs. The craziest part is that a continued increase in centralized control is required to prevent the current financial system from imploding, at least as far as central banks and governments are concerned.
Any alternative would involve giving up some or even all of the central banks' and governments' control over the financial system. They would much rather see the financial system burn to the ground than lose control of it. This is why the IMF has outright recommended countries use CBDCs to fight cryptocurrency adoption to maintain that control. Many institutions are even trying to wipe out the crypto industry.

Cryptocurrency Economics
It depends on the coin or token we're discussing regarding cryptocurrency economics. Bitcoin’s BTC is the obvious choice to reference as an example since it's arguably the biggest crypto competitor to the current financial system. Unlike fiat currencies, BTC has a maximum supply of 21 million. This supply is created slowly over time, and every four years, the amount of new BTC being mined or created is cut in half.
It's believed that the last BTC will be mined around 2140. As basic economics dictates, a gradual decrease in supply combined with the same or more demand results in a higher price. Over the years, Bitcoin has seen exponential adoption that has increased demand, while the new supply of BTC has been declining, resulting in the price action shown below.

BTC’s gradual appreciation in price has incentivized millions of computers to process transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain, which has made it highly decentralized and, therefore, very secure. As a matter of fact, Bitcoin is believed to be the most secure payment network on the planet.
The best part is that as BTC's price continues to climb, the Bitcoin blockchain will only continue to decentralize. This makes it the ideal base layer to build additional financial technologies, and many crypto projects and companies are leveraging the Bitcoin blockchain for its security. Because BTC is increasing in value over time, even relative to Gold, this creates a strong incentive to save rather than spend BTC.
The Custody Difference Between Cryptocurrencies and CBDCs.
With cryptocurrencies, you have the option of self-custody, meaning you can keep your coins and tokens in a digital wallet that you entirely control. Because personal information isn't required to create a cryptocurrency wallet, all cryptocurrency transactions are pseudonymous by default.
Unless you're holding cryptocurrency in your personal crypto wallet, chances are it's being stored in a custodial wallet, which includes cryptocurrency exchanges. This means that the crypto is technically owned by someone else under your name. You might think you have control over your crypto with such a setup, but in reality, the custodian only lets you make transactions so long as you abide by their terms and conditions.
Self-custody simply does not enter into the equation for CBDCs. If all the terms and conditions, or dare I say, restrictions mentioned above, didn't make it clear enough, the central bank will keep all your CBDC holdings and ultimately decide what you can or can't do with your digital money.
Regarding privacy, I reckon this sentence from one of the CBDC reports from the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) sums it up “Full anonymity with CBDCs is not possible.” This is because the central bank needs to be able to track everything specifically to impose these sorts of totalitarian controls.
It goes without saying you’ll be required to complete the KYC protocol. Also, according to the World Economic Forum's Digital Currency report, central banks will assign your digital identity a dystopian social credit score, determining what you can and can't do. The result will be a total absence of privacy with CBDCs, which is a massive problem because privacy is required for financial freedom.
CBDC transactions that don't belong to you will not be viewable, meaning only the central bank can see what's happening behind the scenes. This will also apply at the network level because the technology that underlies a CBDC will likely be a closed source.
A View Of How Both Economic Systems Could Play Out
So what would a cryptocurrency-based economic system look like as opposed to a CBDC-based system? As mentioned above, BTC has been increasing in value over time, even relative to gold, creating a strong incentive to save rather than spend BTC. This makes a BTC-based economy analogous to one where interest rates are consistently high, meaning inflation would be very low or even negative.
Logically, this means a BTC-based economy is also one where it would be more expensive to borrow, and that could limit economic expansion. In a worst-case scenario, this could lead to a deflationary death spiral, where spending decreases, resulting in lower prices, lower production, and so on, until the economy dies.
The thing is that the threat of a deflationary death spiral is nothing more than a ‘fiat currency finance conspiracy theory,’ as evidenced by the fact that the economy has been deflationary for most of human history. This is simply because innovation makes everything cheaper as time goes on, and the deflationary trend only changes whenever a central bank decides to turn the money printer on.

A BTC-based economy also doesn't necessarily require using BTC as the currency. BTC could become the hard money that backs a more elastic currency, the same way gold was used to back national currencies, and that system has worked out pretty well. Ironically, a CBDC-based economy would face the same sort of deflationary risks for similar reasons.
For instance, a CBDC status is considered a safe-haven asset in the eyes of the average investor. Multiple central banks have noted this status as the primary reason they're not rushing with their CBDC rollouts. A CBDC could siphon billions or even trillions of dollars from the traditional financial system. And this includes government bonds, which are also seen as safe-haven assets and considered cash equivalents by experienced investors and regulators alike.
The interest rates on government bonds determine the interest rates in the broader economy, which are dictated by supply and demand. If everyone started selling government bonds for CBDCs because of a financial or geopolitical crisis, this would cause the interest rates in the economy to skyrocket, eventually leading to a next-level, deflationary death spiral and, potentially, even a full-on government default and collapse. Even if central banks programmatically put measures in place to prevent this scenario, a CBDC economy would still put central banks in direct competition with commercial banks.
The Bank for International Settlements admitted in its CBDC report, “a common theme is that maintaining bank profitability would be challenging.” The Bank for International Settlements also determined that the only way a bank could remain profitable would be to raise interest rates. That would make borrowing extremely difficult and result in substandard economic conditions due to deflation.
Although, it seems the financial elite has a solution, and that's a synthetic CBDC, which was defined by the World Economic Forum in their CBDC and stable coin report. A synthetic CBDC would involve having a centralized stablecoin issuer holding the assets backing its stablecoin with a country's central bank. As discussed in this article, the two largest regulated stablecoins are supported almost entirely by cash equivalents, and that’s 'code' for government debt.
This is quite clever because it means everyone buying a regulated stablecoin is financing the US government by indirectly purchasing government debt, which keeps interest rates low and allows its fiat ponzi to continue.

A Positive Note To Wrap Up
After studying various reports and following these topics, there’s arguably no chance CBDCs will reach mass adoption. There are a few reasons for this;
Firstly, the Bank for International Settlements found that only 4-12% of people in developed countries would voluntarily adopt CBDCs. This is significantly lower than the current adoption rates for cryptocurrency. The fact that financial institutions are studying cryptocurrencies to recreate the same adoption curve with CBDCs is evidence of that.
Secondly, the people who know how to create distributed ledger technologies are better off working on a blockchain than a distributed database. Creating a cryptocurrency coin or token that does something useful and valuable can result in astronomical profits and no shortage of social approval. Being involved in creating a CBDC will generate a six-figure salary at best and be seen as the enemy of society in the eyes of many.
Last but not least, central banks are losing the narrative on CBDCs. The awareness of the masses is continually increasing, with hoards of concerned citizens making their voices heard worldwide, physically and virtually, on thousands of truth-seeking internet media.
The more people become aware of how dystopian these CBDCs are, the harder it will be for governments to roll them out. We're already starting to see politicians in the United States and elsewhere propose bills to prevent their central banks from issuing CBDCs, and it's because they are aware their voters don't want the Digital ID/CBDCs.
The “pen is mightier than the sword” is an adage coined in 1839, and this phrase remains commonly known and used 182 years later. Or perhaps we can use a more updated version of a “post is mightier than a gun.” So, get the word out to the unawakened to ensure they know the difference between Central Bank Digital Currencies and honest-to-goodness Cryptocurrencies.
Originally Published @ Markethive.com


